

Chapter 1 Dynamo Tags
This section lists the function, syntax, attributes, and examples for each Dynamo tag.
Use the COMPONENT tag to embed EAServer components in HTML documents.
For SQL access:
<!--COMPONENT ACCESS_METHOD= SQL PKG=packagename COMPONENT_NAME=componentname METHOD=methodname
parameter(s)
-->
For ActiveX access:
<!--COMPONENT ACCESS_METHOD= ACTIVEX PKG=packagename COMPONENT_NAME=componentname METHOD=methodname HOST=hostname
parameter(s)
-->
For Java access:
<!--COMPONENT ACCESS_METHOD= JAVA PKG=packagename COMPONENT_NAME=componentname METHOD=methodname MANAGER_URL=url USERID=id PASSWORD=password NARROW_INTERFACE=narrowinterface
parameter(s)
-->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| ACCESS_METHOD | Can be SQL
, ACTIVEX,
or JAVA
.
The default is SQL
. Determines
the access method to be used for the component.
|
| PKG | Name of the EAServer package. This attribute is required. |
| COMPONENT_NAME | Name of the EAServer component. This attribute is required. |
| METHOD | Name of the component method that is being called. This attribute is required. |
| HOST | The host
and port name to use for the component
HOST=localhost:9000 This attribute is required when using the ACTIVEX
access
method.
|
| MANAGER_URL | The URL to Jaguar Manager. This attribute is optional. If an optional attribute is provided, you must provide all attributes that proceed it. |
| USERID | The ID used for Jaguar Manager. This attribute is optional. If an optional attribute is provided then all attributes preceding it must be provided. |
| PASSWORD | The password for Jaguar Manager. This attribute is optional. If an optional attribute is provided then all attributes preceding it must be provided. |
NARROW_INTERFACE |
The name of the component to which you would like to narrow. This attribute is optional. If an optional attribute is provided then all attributes preceding it must be provided. |
The COMPONENT tag is used to call and manipulate EAServer components. The same attributes associated with the SQL tag may be used with the COMPONENT tag.
The default name of the query object when using the COMPONENT tag is COMPONENT in the same way that the default name of the query object is SQL when the SQL tag is being used.
The following example calls the setMessage method
of a EAServer component. $message
is
equal to saying document.value.message
(passes
in a variable from a form in a previously accessed document):
<!--COMPONENT PKG=Demo_Components COMPONENT_NAME=SharedMsg METHOD=setMessage $message -->
The following example calls the getMajors method of the SVUMetaData component which is part of the SVU package included with EAServer:
<HTML> <!--COMPONENT PKG=SVU COMPONENT_NAME=SVUMetaData METHOD=getMajors --> <!--formatting NAME=COMPONENT--><TR> <!--/formatting--> </HTML>
The following example calls the getMajors method of the SVUEnrollment component which is part of the SVU package included with EAServer. The access method for this example is Java. The GetValue function is used to return the appropriate datatype for each column. For more information on result sets, see the EAServer documentation.
<!--COMPONENT ACCESS_METHOD=JAVA PKG=SVU COMPONENT_NAME=SVUEnrollment METHOD=getMajors MANAGER_URL=iiop://localhost:9000 USERID=jagadmin PASSWORD=""
-->
<!--SCRIPT
function GetValue(query, metadata, column ) {
type = metadata.getColumnType( column );
switch( type ) {
case 1: //CHAR
return query.getString( index );
case 2: //NUMERIC
case 3: //DECIMAL
return query.getBigDecimal( index, this.metadata.getScale(index) ).floatValue();
case 4: //INTEGER
return query.getInt( index );
case 5: //SMALLINT
return query.getShort( index );
case 6: //FLOAT
case 7: //REAL
return query.getFloat( index );
case 8: //DOUBLE
return query.getDouble( index );
case 12: //VARCHAR
return query.getString( index );
case 0: //NULL
return null
case 1111: //OTHER
return query.getObject( index );
case 91: //DATE
return query.getDate( index );
case 92: //TIME
return query.getTime( index );
case 93: //TIMESTAMP
return query.getTimestamp( index );
default:
if( type < 0 ) {
if( type == -1 ) { //LONGVARCHAR
return query.getString( index );
} else if( type == -2 ) { //BINARY
return query.getBytes( index );
} else if( type == -3 ) { //VARBINARY
return query.getBytes( index );
} else if( type == -4 ) { //LONGVARBINARY
return query.getBytes( index );
} else if( type == -5 ) { //BIGINT
return query.getLong( index );
} else if( type == -6 ) { //TINYINT
return query.getShort( index );
} else if( type == -7 ) { //BIT
return query.getBytes();
}
} else {
return query.getBytes( index );
}
}
document.writeln( "<H3>Testing SVUEnrollment getmajors</H3>" );
//The result of the tag is stored in the variable
//COMPONENT
prequery = COMPONENT;
//The RecordSet returned needs to fixed using a
//static method call
query = java.CallStaticMethod( "com.sybase.CORBA.jdbc11.SQL","getResultSet",prequery );
received = query.next();
i = 0;
while( received ) {
metadata = query.getMetaData();
for( j = 1; j <= 3; j++ ) {
value = GetValue( query, metadata, j );
document.writeln( value );
}
received = query.next();
i++;
}
-->
"Calling EAServer Component Methods from PowerDynamo" in the PowerDynamo User's Guide
The DATA tag allows an undetermined number of rows to be returned from a query.
<!--DATA [ QUERY=queryname ] [ NAME=colname ] -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| QUERY | Allows you
to specify the name of a query from which the data should be extracted.
If you do not provide the QUERY
attribute,
the default is "SQL".
<!--DATA QUERY = myquery--> |
| NAME | Allows you to specify
the name of a column from which the data should be extracted. This
attribute is optional. If you do not provide a NAME
,
sequential DATA tags will correspond to the order of the columns
in the query result set.
<!--DATA NAME = city--> |
When you use a query in a template, and the results are to be formatted as a table or list, you do not know how many rows will be in the result set.
PowerDynamo uses data placeholders, formatted as comment tags, to describe the formatting of each row of the query result set. The DATA tag is used in conjunction with the FORMATTING tag.
The data placeholders are marked with comment tags:
<!--DATA-->
Only one row of placeholders is included within a FORMATTING statement. The application server automatically expands the placeholder to as many rows as required to hold the result set.
DATA tags must be between a FORMATTING start tag and a FORMATTING end tag.
The following template fragment defines a table that holds the results of a simple query:
<TABLE BORDER> <TR> <TH>name</TH> <TH>color</TH> </TR> <!--FORMATTING--><TR> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> </TR><!--/FORMATTING--> </TABLE> </BODY> </HTML>
The DOCUMENT tag allows you to set certain properties of the document, such as the content type, status, whether or not the request should be redirected to an alternate URL, and the duration of time, if any, the request output should be cached.
<!--DOCUMENT [ CONTENT_TYPE = type ]
... [ REDIRECT = URL ]
... [ STATUS = statusCode ]
... [ CACHED_OUTPUT_TIMEOUT = minutes ] -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| CONTENT_TYPE | The MIME
type of document being returned to the browser, for example, image/gif.
<!--DOCUMENT CONTENT_TYPE="image/gif"--> This attribute is optional. |
| REDIRECT | The name
of the URL to which the current request should be redirected.
This attribute is optional. |
| STATUS | The status
of a document where the first three characters represent a three-digit
status code and the remaining characters contain a brief explanation
of the status. For example, 204 No Response
.
This attribute is optional. |
| CACHED_OUTPUT_TIMEOUT | Duration of time (in minutes) for which the generated output of a script or template will be cached. This attribute is optional. The default is 0. |
This example caches the document output for five minutes.
<HTML> <TITLE>doctag.stm</TITLE> <BODY> <H1>Customer Phone Numbers</H1> <!--SQL SELECT customer.fname, customer.lname, customer.phone FROM DBA.customer customer --> <!--DOCUMENT CACHED_OUTPUT_TIMEOUT = "5" --> <TABLE BORDER> <TR> <TH>fname</TH> <TH>lname</TH> <TH>phone</TH> </TR> <!--formatting--><TR> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> </TR><!--/formatting--> </TABLE> </BODY> </HTML>
The ELSE tag allows you to manipulate script flow. If none of the preceding conditions are true, the request associated with the ELSE statement is executed.
<!--ELSE -->
This example uses the IF tag to check if a condition (YearOfBirth=1970) is true or false. If the condition is true the text "You are old enough to participate in this promotion" displays. If the condition is false, the ELSE tag is used and displays "You are not old enough to participate in this promotion."
<HTML> <!--SCRIPT YearOfBirth=1970; --> <!--IF EXPR="YearOfBirth < 1979" --> You are old enough to participate in this promotion. <!--ELSE--> You are not old enough to participate in this promotion. <!--ENDIF--> </HTML>
The ELSEIF tag can be used after an IF tag to check another condition if the first condition associated with the IF tag was false.
<!--ELSEIF EXPR = expression -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| EXPR | The expression determines whether the execution of the tag should continue or be passed over. If the expression is true, execution continues. |
An example of the ELSEIF tag is as follows:
<HTML>
<!--SCRIPT
var num=22;
-->
<!--IF EXPR="num > 5" -->
<!--IF EXPR="num > 10" -->
num is greater than 10
<!--ELSEIF EXPR="num < 10"-->
num is greater than 5 and less than 10
<!--ELSE-->
num is 10
<!--ENDIF-->
<!--ENDIF-->
</HTML>
The ENDIF tag ends the IF block.
<!--ENDIF -->
The following example has two IF blocks that end with the ENDIF tag:
<HTML>
<!--SCRIPT
var num=22;
-->
<!--IF EXPR="num > 5" -->
<!--IF EXPR="num > 10" -->
num is greater than 10
<!--ELSEIF EXPR="num < 10"-->
num is greater than 5 and less than 10
<!--ELSE-->
num is 10
<!--ENDIF-->
<!--ENDIF-->
</HTML>
The EVALUATE tag allows you to evaluate a DynaScript expression.
<!--EVALUATE EXPR = expression -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| EXPR | The expression to be evaluated. This attribute is required. |
An example of the EVALUATE tag is as follows:
<!--EVALUATE EXPR="j + 1" --> dollars.
If j is equal to 5, the above example would have an output of:
6 dollars
The EXECUTE tag allows you to execute a system command.
<!--EXECUTE COMMAND = commandname -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| COMMAND | The name of the command to be executed. This attribute is required. |
This example launches notepad.exe:
<!--EXECUTE command = "notepad.exe"-->
Defines the output of a query.
For HTML formatting:
<!--FORMATTING [[FORMAT_AS="HTML" ][ BORDER = borderwidth ] [ LIST = listtype ][ MAXROWS = num ] [ NAME = stmtname ] [STARTROW = rownum ][STRIP_TRAILING_BLANKS]] -->
<!--/FORMATTING -->
For XML formatting:
<!--FORMATTING [[FORMAT_AS="XML"] [RESULTSET_TAG=restultsettagname][ROW_TAG=rowtagname][COLUMN_TAG=columntagname][USE_CDATA ] [ MAXROWS = num ] [ NAME = stmtname ] [STARTROW = rownum ] [STRIP_TRAILING_BLANKS]] -->
<!--/FORMATTING -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| BORDER | The width
of the table border. A value of 0 creates a table with no border. BORDER
applies
only if you use the default formatting, that is, nothing between
the <!--FORMATTING-->
and <!--/FORMATTING-->
tags.
If you specify both BORDER
and LIST
, LIST
takes precedence.
|
| LIST | Use LIST
if
you want the query to display in a list. LIST
may
be set to ORDERED
, UNORDERED
,
or DEFINITION
.
LIST
only
applies if you use default formatting, that is, you place nothing
between the <!--/FORMATTING-->
tags.
If you specify both BORDER
and LIST
, LIST
takes precedence.
<HTML> <TITLE>format.stm</TITLE> <BODY> <H1></H1> <!--SQL SELECT customer.fname, customer.lname FROM DBA.customer customer --> <!--FORMATTING LIST=ORDERED--> <!--/FORMATTING--> </BODY> </HTML> |
| MAXROWS | The maximum
number of times the content between the start and end tag is to
be repeated. This attribute is optional.
Normally, the formatting tag causes the content between the <!--FORMATTING--> and the <!--/FORMATTING--> tag to be repeated for each row in a query result. The addition of the MAXROWS attribute causes the content between the start and end tag to be repeated at most MAXROWS times. |
| NAME | The name
of the SQL statement to be formatted. If you do not provide the
NAME attribute, the name "SQL" is the default.
If you have more than one SQL statement in a template, you can ensure that your formatting statements refer to the correct SQL statement by referencing the name of the SQL statement in a FORMATTING tag attribute. For example, this statement formats the results of the SQL statement ProductQuery: <!--FORMATTING NAME=ProductQuery--> |
| STARTROW | Indicates
the row of the result set to begin from when displaying. Set STARTROW
to an integer greater than or equal to 0.
<!--FORMATTING STARTROW=4 BORDER=2 --> |
| FORMAT_AS | May be set
to HTML (the default) or XML. If set to XML, the additional tags
RESULTSET_TAG, ROW_TAG and COLUMN_TAG
can be used to generate XML output. The BORDER and LIST attributes
do not apply.
The attributes NAME, MAXROWS, and STARTROW apply for both XML and HTML. |
| RESULTSET_TAG | Sets the
tag surrounding the result set. If you do not specify a RESULTSET_TAG,
the default tag is SYBRESULTSET .
This attribute applies only when FORMAT_AS=XML. |
| ROW_TAG | Specifies
the tags to be used to define a table row. If no ROW_TAG
is specified, the default tag of SYBROW is used.
This attribute applies only when FORMAT_AS=XML. |
| COLUMN_TAG | Specifies
the tags to be used to define a table column. If no COLUMN_TAG
is specified, the column's label is used.
This attribute applies only when FORMAT_AS=XML. |
| USE_CDATA | Instructs
Dynamo to encode characters using CDATA to escape special XML characters.
If you do not specify USE_CDATA, characters are encoded
with the normal ampersand method.
This attribute applies only when FORMAT_AS=XML. |
| STRIP_TRAILING_BLANKS | Strips trailing blanks from query data. By default, this attribute is not used. This attribute is useful when used with output generated from Adaptive Server Enterprise or other databases that have trailing blank characters. |
When you use a query in a template, and want the results to be formatted as a table or list, you do not know ahead of time how many rows are going to be in the result set.
PowerDynamo uses data placeholders to describe the formatting of each row of the query result set.
Formatting using scripts
You can also use embedded scripts
to format output. The flexibility of scripts allows more varied
formatting than the formatting tags.
The HTML tags for formatting instructions are slightly different from the tags used for SQL statements. To allow an HTML editor to modify and refine the actual formatting, the formatting description is not inside a comment. Instead, comment tags are used for placeholders for the data, which are replaced on processing by the actual data.
All data placeholders must be between formatting start and end comment tags. The start tag is:
<!--FORMATTING-->
The end tag is:
<!--/FORMATTING-->
There is no restriction on the HTML code that can be included between the tags. The formatting comment tags have no effect on HTML that occurs between them; they affect only the embedded instructions.
This example defines a table that holds the results of a simple query:
<TABLE BORDER> <TR> <TH>name</TH> <TH>color</TH> </TR> <!--FORMATTING--><TR> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> </TR><!--/FORMATTING--> </TABLE>
This example performs a query on a product
table with more than 100 product codes. Using the MAXROWS
attribute
results in only the first 3 product codes being returned.
<!--SQL select code from productlist --> <!--FORMATTING MAXROWS=3--> Product code: <!--DATA--> <!--/FORMATTING -->
has the output of:
Product code: 111 Product code: 222 Product code: 333
You can nest the FORMATTING
tag
inside other FORMATTING
tags.
For example, this fragment:
<!--FORMATTING NAME=Query1-->
<!--FORMATTING NAME=Query2-->
<!--DATA QUERY=Query1--><!--DATA-->
<!--/FORMATTING-->
<!--/FORMATTING-->
has an output similar to:
Fred 26 Fred 32 Fred 27 Fred 34 Jane 26 Jane 32 Jane 27 Jane 34
If you do not specify a QUERY attribute on the DATA tag, the query specified on the innermost <!--FORMATTING--> block is assumed.
Using nested FORMATTING statements on databases that do not support backward cursor movement causes performance degradation. Sybase strongly recommends that you not nest FORMATTING sections unless absolutely necessary.
You can also reference a query that is outside of the formatting block. For example:
<!--formatting NAME=Query1-->
<!--data QUERY=Query3 NAME=title--><!--DATA-->
<!--/formatting-->
This example uses the FORMAT_AS=XML tag to create the output in XML.
<!--SQL select product.description, product.color from product order by product.description --> <!--FORMATTING FORMAT_AS="XML" RESULTSET_TAG="MYRESULTSET" ROW_TAG="MYROW" COLUMN_TAG="MYDESCRIPTION MYCOLOR"--> <!--/FORMATTING-->
The output looks like:
<MYRESULTSET> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Cloth Visor</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>White</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Cotton Cap</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Black</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Cotton Shorts</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Black</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Crew Neck</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Black</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Hooded Sweatshirt</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Green</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Plastic Visor</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Black</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Tank Top</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>White</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>V-neck</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Orange</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Wool cap</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>White</MYCOLOR></MYROW> <MYROW><MYDESCRIPTION>Zipped Sweatshirt</MYDESCRIPTION><MYCOLOR>Blue</MYCOLOR></MYROW> </MYRESULTSET>
The IF tag allows for manipulation of script flow. If the condition associated with the tag is true the text associated with the IF tag is executed.
<!--IF EXPR=expression -->
<!--ENDIF -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| EXPR | The expression that determines whether the execution of the tag should continue or be passed over. If the expression is true, execution will continue. |
This example uses the IF tag to check if a condition (YearOfBirth < 1979) is true or false. If the condition is true the text "You are old enough to participate in this promotion" displays. If the condition is false, the else statement is used and displays "You are not old enough to participate in this promotion."
<HTML> <!--SCRIPT YearOfBirth=1970; --> <!--IF EXPR="YearOfBirth < 1979" --> You are old enough to participate in this promotion. <!--ELSE--> You are not old enough to participate in this promotion. <!--ENDIF--> </HTML>
Use the INCLUDE tag to include the generated output of another document. You can specify a relative or an absolute path, or you can use the tilde (~) character.
For information on using the tilde character, see "Paths".
<!--INCLUDE NAME = filename -->
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
NAME
|
Name of the document that is to have its output included in the output of the current document. |
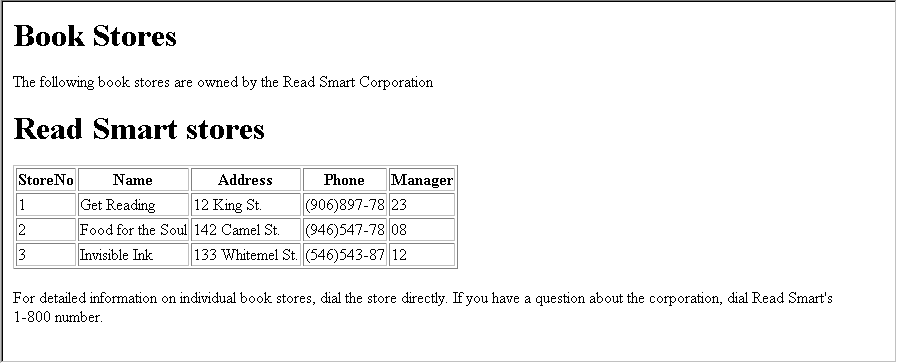
<HTML>
<TITLE>sample.stm</TITLE>
<BODY>
<H1>Book Stores</H1>
<P>The following book stores are owned by the Read Smart Corporation</P>
<!--INCLUDE name="stores.stm"-->
<P>For detailed information on individual book stores, dial the store directly. If you
have a question about the corporation, dial Read Smart's 1-800 number. </P>
</BODY>
</HTML>
The LABEL tag allows you to return the column name or column alias (as specified in the SQL query) for the colNum column.
<!--LABEL [ NAME = queryname ][ INDEX = columnindex ] -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
NAME
|
The name
of the query. If you do not specify NAME
,
the name "SQL" is assumed.
|
INDEX
|
The column index. This attribute is optional. |
You can use the LABEL tag alone or from within a formatting section. When you use it within a formatting section for a query, each subsequent occurrence of the LABEL tag increases the value of INDEX by one.
The following lines:
<!--SQL
select name, color, size from product
-->
<!--FORMATTING-->
<!--LABEL-->: <!--DATA-->
<!--LABEL-->: <!--DATA-->
<!--LABEL-->: <!--DATA-->
<!--/FORMATTING-->
produce the following output:
name: Tee Shirt color: White size: Small name: Tee Shirt color: Orange size: Medium name: Tee Shirt color: Black size: One size fits all
Use the MAILPIECE tag to send mail through an SMTP host.
<!--MAILPIECE TO = recipientAddress [ FROM = fromAddress ] [ SUBJECT = subject ] [ SMTPHOST = SMTPAddress ] -->
Body of the mail piece
<!--/MAILPIECE -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| TO | The address of the recipient of the mail piece. This attribute is required. |
| FROM | The address of the person sending the mail piece. This attribute is optional. |
| SUBJECT | The subject of the mail piece. This attribute is optional. |
| SMTPHOST | The SMTP host of the mail piece. This attribute is optional. If not specified here, the SMTP host must be set from the Default General Settings folder in Sybase Central™. |
| INDEX | The column index. This attribute is optional. |
Use the MAILPIECE tag to send mail from PowerDynamo using Dynamo tags and a SMTP host. Enter the body of the mail piece between the start and end mail piece tag. If you do not specify an SMTP host within the script, the default SMTP host specified in Sybase Central is used. If you have not specified an SMTP host in either of these places, an error occurs.
This example sends a mail piece with a subject and body. The SMTP host has been set in Sybase Central:
<HTML> <!--MAILPIECE TO="elmo@sybase.com" FROM="fred@sybase.com" SUBJECT="My mail piece subject"--> This is the body of the mail piece. <!--/MAILPIECE--> </HTML>
Use the SCRIPT tag to embed DynaScript in HTML documents.
<!--SCRIPT
DynaScript code
-->
All DynaScript scripts begin and end with a
SCRIPT tag (<!--SCRIPT
-->
).
All information within a SCRIPT tag is invisible to any Web editing tool-in other words, it is processed by the Dynamo application server.
This example embeds the DynaScript method document.WriteLn
in
an HTML document:
<HTML>
<TITLE>sample.stm</TITLE>
<BODY>
<H1>DynaScript Sample</H1>
<!--SCRIPT
document.WriteLn("This is DynaScript");
-->
For more information, see Chapter 2, "The DynaScript Language"
Use the SQL tag to embed SQL statements that are embedded in HTML documents.
<!--SQL [ NAME = queryname ]
... [ CONNECTION_NAME = conname
... | CONNECTION_OBJECT = objname
... | DSN = datasource UID = userid- PWD = password
... | SERVER = servername DBN = databasename UID = userid PWD = password ]
... [ NO_EXECUTE = queryname ]
[ NO_SQL_ERROR ]
SQL query
-->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| NAME | Name of a query. This attribute is optional. If you do not use NAME, then "SQL" is the default. |
| CONNECTION_NAME | Name of the
connection that the SQL query is to use. This attribute is optional.
By default, SQL queries use the connection name associated with the document in which they are contained. The CONNECTION_NAME attribute enables you to explicitly specify the connection name that you would like a SQL query to use. The SQL CONNECTION_NAME tag is used as follows:
<!--SQL CONNECTION_NAME="MyConnection"
select * from product
-->
The Connections folder of Sybase Central contains a list of PowerDynamo connection names. |
| CONNECTION_OBJECT | Name of the
DynaScript connection object that the SQL query is to use. This
attribute is optional:
<!--SQL CONNECTION_OBJECT=connObj select * from product --> |
| NO_EXECUTE | Allows you
to prepare a query without executing it.
<!--SQL NAME=myQuery NO_EXECUTE
select * from product
-->
To execute the query you would do something like:
<!--SCRIPT
myQuery.Execute();
-->
|
| DSN, UID, PWD | The data
source name that you would like a SQL query to use. Using a data
source name to connect to a database bypasses both connections and
connection objects. No connection names are created or used. The user
ID and password are optional. For example:
<--SQL DSN="PowerDynamo Demo" UID=dba PWD=sql
select * from product
-->
|
| SERVER, DBN, UID, PWD | The server
name on which the SQL query should be executed. The connection made
to the server will be an Open Client connection.
The SERVER, DBN, UID, and PWD attributes are used as follows:
<!--SQL SERVER="myserver" DBN="mydatabase" UID=dba PWD=sql
select * from product
-->
Using a server name to connect to a database bypasses both connections and connection objects. No connection names are created or used. DBN is optional. If you do not specify a database name, the connection uses the user's default database. |
| NO_SQL_ERROR | Executes a script even if an error is encountered. No error is displayed in the output. To display any resulting errors, use the SQL_ON_ERROR tag. |
Only one connection
You can use only one of: CONNECTION_NAME,
CONNECTION_OBJECT, DSN, or SERVER.
Use SQL queries to access and manipulate data that has been stored in a database.
This example has a SQL query embedded in HTML:
<HTML>
<TITLE>sample.stm</TITLE>
<BODY>
<H1>DynaScript Sample</H1>
<!--SQL
SELECT Book.Title, Book.BookID, Book.Price
FROM DBA.Book Book
-->
</BODY>
</HTML>
Performs an insert operation using the document's parameters.
<!--SQL_INSERT TABLE= tableName [ NAME = queryname ]
... [ CONNECTION_NAME = conname
... | CONNECTION_OBJECT = objname
... | DSN = datasource UID = userid- PWD = password
... | SERVER = servername DBN = databasename UID = userid PWD = password ]
... [ NO_EXECUTE = queryname ]
[ NO_SQL_ERROR ]
-->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| TABLE | Name of the table that the data is to be inserted in. This attribute is required. |
| NAME | Name of a SQL query. This attribute is optional. If no NAME is provided then the name "SQL" is assumed. |
| CONNECTION_NAME | Name of the
connection that the SQL query is to use. This attribute is optional.
By default, SQL inserts use the connection name associated with the document in which they are contained. The CONNECTION_NAME attribute enables you to explicitly specify the connection name that you would like a SQL insert to use. For example: <!--SQL_INSERT CONNECTION_NAME="MyConnection" TABLE="product" --> You can find a list of PowerDynamo connection in the Connections folder of Sybase Central. |
| CONNECTION_OBJECT | Name of the DynaScript connection object that the SQL query is to use. This attribute is optional. |
| DSN, UID, PWD | The data
source name that you would like a SQL query to use. Using a data
source name to connect to a database bypasses both connections and
connection objects. No connection names are created or used.The
user ID and password are optional. For example:
<!--SQL_INSERT DSN="PowerDynamo Demo" UID=dba PWD=sql TABLE="product"--> |
| SERVER, DBN, UID, PWD | The server
name on which the SQL query should be executed. Using a server name
to connect to a database bypasses both connections and connection
objects. No connection names are created or used. The connection made
to the server is an Open Client connection.
The SERVER, DBN, UID, and PWD attributes are used as follows: <!--SQL SERVER="myserver" DBN="mydatabase" UID=dba PWD=sql TABLE="product"--> DBN is optional. If you do not specify a database name, the connection uses the user's default database. |
| NO_EXECUTE | Allows you
to prepare a SQL query without executing it:
<!--SQL_INSERT NAME=myQuery NO_EXECUTE TABLE="product"--> To execute the query, you would do something like:
<!--SCRIPT
myQuery.Execute();
-->
|
| NO_SQL_ERROR | Causes a script to execute even if an error is encountered. No error is displayed in the output. To display errors, use the SQL_ON_ERROR tag. |
Only one connection
You can use only one of: CONNECTION_NAME,
CONNECTION_OBJECT, DSN, or SERVER.
Use SQL_INSERT to enter data into a table. For example, lets's say you have created a form that asks a user to enter the information to add to the table. If the names on the form match the names of the table columns, you can insert the information into the table by calling a simple script that includes:
<!--SQL_INSERT TABLE="tablename"-->
The following template allows a user to add a new product to the database. The first document (newProduct.stm) collects the information and passes it to the second document (insert.ssc) for insertion.
<HTML> <TITLE>newProduct.stm</TITLE> <BODY> <H1>New Product</H1> <P>Enter the following information</P> <FORM METHOD=POST ACTION="insert.ssc"> <OL> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="id" >ID of the product<BR> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="name" >Name of the product<BR> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="description" >Description<BR> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="size" >Size<BR> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="color" > Color<BR> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="quantity" > Quantity<BR> <LI><INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="unit_price" > Price<BR> </OL> <P><INPUT TYPE="submit"></p> <P><INPUT TYPE="RESET" VALUE="Clear Form"></P> </FORM> </BODY> </HTML>
calls:
<HTML> <TITLE>insert.ssc</TITLE> <BODY> <H1>DynaScript Sample</H1> <!--SQL_INSERT TABLE="product" --> </BODY> </HTML>
The above example would be equivalent to:
<!--SQL
insert into product ( id, name, description, size, color, quantity, unit_price )
values ( 999, 'dog', 'furry', 'dog_sized', 'brown', 1, 123 )
-->
The SQL condition tags allow you to specify a certain condition that must be fulfilled for the code between the conditional start and end tags to be executed.
<!--SQL_ON_type [ NAME = queryname ]-->
<!--/SQL_ON_type -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| NAME | Name of a query. This attribute is optional. If you do not provide a query name, "SQL" is the default. |
type:
NO_ERROR | ERROR | NO_ROWS | ROWS
The following table lists the conditions that are supported by Dynamo. If the condition is fulfilled, the source between the conditional start and end tag is included in the output.
| Start tag | End tag | Condition |
|---|---|---|
<!--SQL_ON_NO_ERROR-->
|
<!--/SQL_ON_NO_ERROR-->
|
Query did not produce an error. |
<!--SQL_ON_ERROR-->
|
<!--/SQL_ON_ERROR-->
|
Query produced an error. |
<!--SQL_ON_NO_ROWS-->
|
<!--/SQL_ON_NO_ROWS-->
|
Result set did not produce any rows. |
<!--SQL_ON_ROWS-->
|
<!--/SQL_ON_ROWS-->
|
Result set produced at least one row. |
You can use one or more types of tags (SQL, SCRIPT, and so on.) between a conditional start and end tag.
This example provides output only if the SQL query does not produce an error:
<!--SQL
select Fname, Lname, accno, amount
from savings where accno = :account
-->
<!--SQL_ON_NO_ERROR-->
<!--SCRIPT
document.WriteLn("You have " + account.amount + " in your account.");
-->
<!--/SQL_ON_NO_ERROR-->
The SQL_ERROR_CODE tag allows you to return the current error code. If a SQL instruction is carried out successfully, an error code of 0 is returned.
<!--SQL_ERROR_CODE [ NAME = queryname ] -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
NAME
|
Name of a query. This attribute is optional. If you do not provide a query name, "SQL" is assumed. |
This example returns 0 as well as the output generated from the SQL query as long as no errors are encountered during execution.
<!--SQL SELECT Stock."Quantity", Stock."BookID" FROM "DBA"."Stock" Stock --> <!--SQL_ERROR_CODE--> <TABLE BORDER> <TR> <TH>Quantity</TH> <TH>BookID</TH> </TR> <!--formatting--><TR> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> <TD><!--DATA--></TD> </TR><!--/formatting--> </TABLE> </BODY> </HTML>
The SQL_ERROR_INFO tag allows you to return a description of the error information.
<!--SQL_ERROR_INFO [ NAME = queryname ] -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
NAME
|
Name of a query. This attribute is optional. If you do not provide a query name, "SQL" is the default. |
This example displays error information for
a query named myQuery
:
<!--SQL NAME=myQuery
select lname, fname from customer
-->
<!--SQL_ERROR_INFO NAME="myQuery" -->
<!--SCRIPT
while (myQuery.MoveNext()) {
document.WriteLn(myQuery.GetValue(1) + "," + myQuery.GetValue(2));
}
myQuery.MoveFirst();
-->
The SQL_STATE tag returns the current SQL state of a query.
<!--SQL_STATE [ NAME = queryname ] -->
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
NAME
|
Name of a query. This
attribute is optional. If you do not provide a query name, "SQL" is
the default.
<!---SQL_STATE NAME="myquery"--> |
This example displays the state of the SQL query:
<!--SQL
select lname, fname from customer
-->
<!--SQL_STATE-->
<!--SCRIPT
while (SQL.MoveNext()){
document.WriteLn(SQL.GetValue(1) + "," + SQL.GetValue(2));
}
-->
| Copyright © 2001 Sybase, Inc. All rights reserved. |

| |